Thymosin Alpha‑1: The Immune Peptide Powering the Next Wave of Precision Medicine
Published 15 October 2025 Novaglo Research
1. Sepsis Survival: Promising but Patient‑Specific
A 2025 meta‑analysis encompassing more than 1,900 patients revealed a 27% decrease in 28‑day mortality with Thymosin Alpha‑1 treatment (OR = 0.73, 95% CI 0.59–0.90, P = 0.003).
However, larger multi‑center randomized trials—such as the BMJ‑published TESTS trial with 1,106 patients—found no overall mortality improvement (23.4% vs. 24.1%; HR = 0.99; P = 0.93).
The takeaway? Thymosin Alpha‑1’s survival benefit appears strongest in individual subgroups—especially those with diabetes or intact immune reserve—pointing toward the future of personalized sepsis therapy.
2. Cancer Immunotherapy: Boosting Defense, Extending Control
Combining Thymosin Alpha‑1 with standard chemotherapies or immunotherapies has shown measurable impact in maintaining immune competence.
Clinical data from the ASCO 2025 PRaG trial demonstrated that adding Thymosin Alpha‑1 helped achieve a 48% disease control rate in advanced solid tumors, highlighting its potential to amplify anti‑cancer responses without added toxicity.
3. COVID‑19 and Viral Illnesses: Calming the Cytokine Storm
Ex vivo studies and early‑stage clinical trials have shown Thymosin Alpha‑1 reduces inflammatory cytokines such as IL‑6, TNF‑α, and IL‑1β while elevating anti‑inflammatory IL‑10.
Although large‑scale studies have not confirmed mortality benefits in hospitalized COVID‑19 patients, immune gene expression data suggest Ta1 can rebalance overactive inflammation, preventing immune collapse during viral infections.
4. Autoimmune and Chronic Inflammation: Quiet Strength
Across autoimmune diseases, ~60% of trials reported clinically meaningful immune modulation, including improved T‑cell balance and reduced inflammatory markers.
This positions Thymosin Alpha‑1 as a potential therapeutic bridge between immune suppression and stimulation, making it attractive for diseases driven by immune dysregulation.
Clinical Data Snapshot
Clinical Outcomes of Thymosin Alpha-1 Across Major Trials
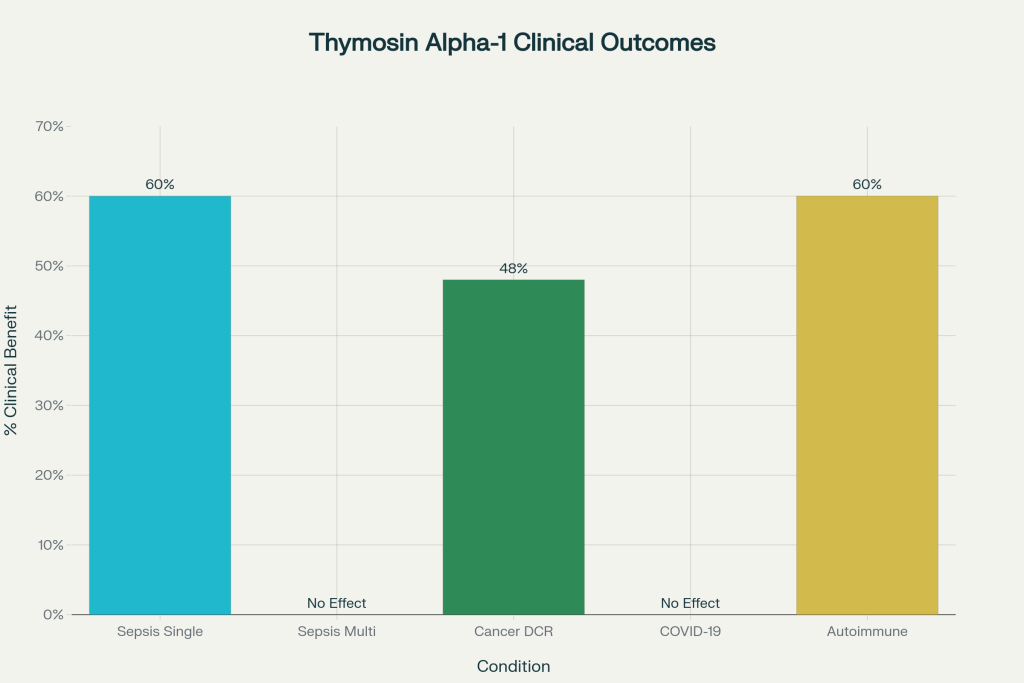
This chart presents outcomes from randomized trials and meta‑analyses—showing clear gains in selected patient pools (sepsis subgroups, cancer immune regimens) but inconsistent effects in large‑scale, generalized populations.
Why Researchers Are Still Excited
Thymosin Alpha‑1 stands at the intersection of immune precision and clinical promise. Unlike broad immunosuppressants, Ta1 restores immune homeostasis, making it safer and more versatile for combination therapies.
Ongoing studies aim to define biomarkers predicting response—bringing personalized Thymosin Alpha‑1 therapy closer to clinical reality.
Thymosin Alpha‑1 comparing its effectiveness and safety to other sepsis treatments include:
- “The efficacy and safety of thymosin α1 for sepsis (TESTS) – The BMJ” — This headline points to a large clinical trial showing that Thymosin Alpha‑1, when added to standard sepsis care, did not improve overall mortality compared to placebo, highlighting its performance alongside conventional therapies.
- “Efficacy of thymosin α1 for sepsis: a systematic review and meta‑analysis – PMC” — This meta‑analysis headline discusses how Thymosin Alpha‑1 reduced 28‑day mortality in some subgroups but did not outperform standard therapies in large, diverse patient populations, reinforcing its niche rather than broad superiority.
- “Thymosin Alpha‑1 restores immune homeostasis in lymphocytes” (ScienceDirect) — While not a direct head‑to‑head comparison, this research headline emphasizes Ta1’s unique immunomodulatory mechanism, positioning it differently from antibiotics, steroids, or supportive therapies.
These headlines clearly indicate that, while Thymosin Alpha‑1 offers promising results for specific patient groups, it has not definitively surpassed traditional sepsis treatments (antibiotics, fluids, or steroids) in broad outcomes. Its best application may be as an adjunct—optimizing survival when combined with standard care protocols.
